Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are more than just a painful inconvenience; they affect millions of people each year, making it essential to unravel the mysteries behind these common ailments. In this blog post, we embark on a journey to demystify UTIs, shedding light on their origins, symptoms, and ways to safeguard your urinary health
What are Urinary Tract Infections(UTI)
A urinary tract infection is an infection in any part of your urinary system, which includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. UTIs are most common in the bladder (cystitis) and urethra (urethritis).
UTIs are caused by bacteria, which can enter the urinary tract through the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. Bacteria can also enter the urinary tract from the bloodstream.
The Root Causes of UTIs
The root cause of UTIs is bacteria entering the urinary tract. The most common type of bacteria that causes UTIs is Escherichia coli (E. coli). E. coli is a type of bacteria that normally lives in the intestines. However, it can sometimes travel to the urethra and into the bladder, where it can cause an infection.
Other types of bacteria that can cause UTIs include:
- Staphylococcus saprophyticus
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Proteus mirabilis
- Enterococcus faecalis
Bacteria can enter the urinary tract in a number of ways, including:
- Sexual activity: During sexual activity, bacteria from the rectum or vagina can be pushed into the urethra.
- Poor hygiene: Not wiping from front to back after using the toilet can increase the risk of bacteria spreading from the rectum to the urethra.
- Using a catheter: A catheter is a tube that is inserted into the bladder to drain urine. People who use catheters have a higher risk of UTIs because the catheter can allow bacteria to enter the bladder.
- Weakened immune system: People with a weakened immune system, such as people with diabetes or HIV/AIDS, are more likely to develop UTIs.
- Structural abnormalities in the urinary tract: Some people have structural abnormalities in their urinary tract that make it more difficult for urine to drain properly. This can lead to a buildup of urine in the bladder, which can increase the risk of UTIs.
The Red Flags: How Do You Recognize a Uti?
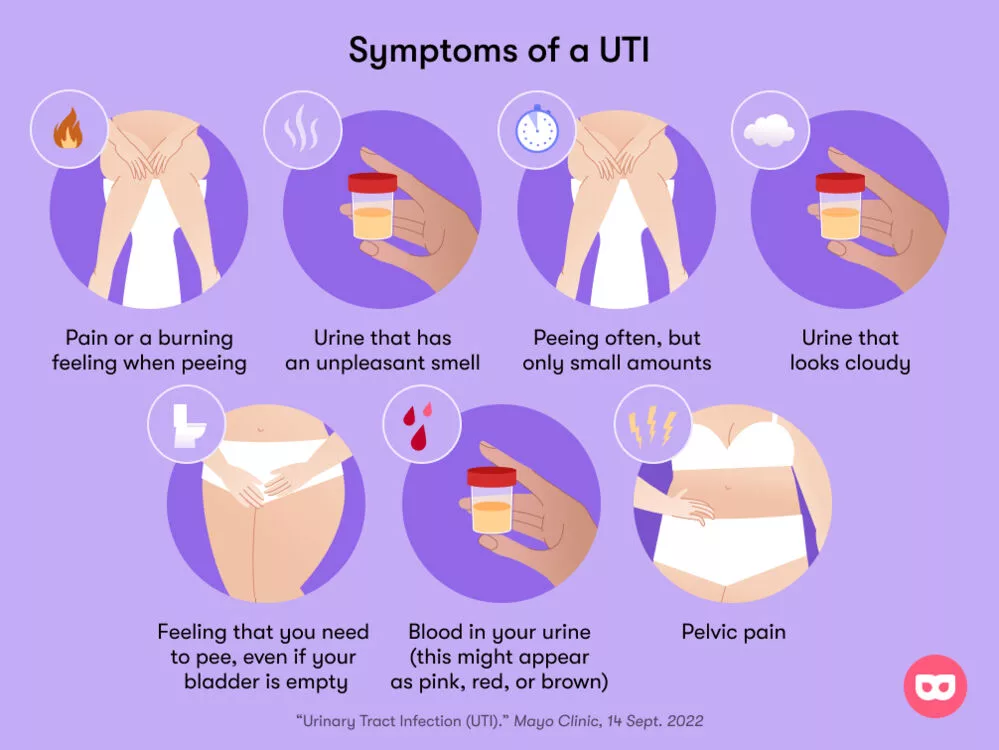

- Pay attention to your urination habits. If you have a sudden urge to urinate more often than usual, or if you feel like you can’t completely empty your bladder, it could be a sign of a UTI.
- Notice the appearance of your urine. If your urine is cloudy, bloody, or has a strong smell, it could be a sign of a UTI.
- Pay attention to any pain or discomfort you feel when urinating. If you feel pain or burning when you urinate, it could be a sign of a UTI.
- Be aware of any other symptoms you may be experiencing, such as back pain, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, chills, or loss of appetite. These symptoms can also be signs of a UTI.
Seeking Answers? Steps to Take
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are usually treated with antibiotics. The type of antibiotic and the length of treatment will depend on the severity of the infection. In most cases, UTIs can be cured with a short course of antibiotics.


A Natural Remedy: Akam Infection Cleanser for UTIs
Beyond conventional treatments, some individuals explore natural remedies for managing UTIs. Akam Infection Cleanser is a unique herbal blend that has gained recognition for its potency in alleviating UTI symptoms. It incorporates herbal ingredients with a history of traditional use in supporting urinary health.
Akam Infection Cleanser offers several benefits for those dealing with UTIs, including symptom relief, antimicrobial properties, and overall well-being. While it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for any medical condition, many individuals have found comfort in complementing their treatment with natural alternatives like Akam Infection Cleanser.
